|
|
Automating Online Dispute Resolution for
B2B using multi-agent systems,
TD7, CNCSIS-534, 2007-2008
Online Dispute Resolution
|
|
Online
Dispute Resolution (ODR) is promised to
become an important method to settle
e-commerce disputes. To reach this statute
it needed ten years of fast and sustained
development [Tyler, 2003]: starting in 1996
as a hobby, an experimental stage sustained
by academics and non-profit organizations
during 1997-1998, an entrepreneurial stage
from 1999 (the rate of success as business
is 75%), and beginning with 2003 there have
been a lot of governmental efforts and
projects to institutionalize the online
dispute resolution process. Initially, it
started in the USA, followed by Australia,
where even automatic ODR systems are
functioning under a legal framework (for
distributing the marital property in divorce
cases), now Europe gives a sensitive
attention to ODR systems.
|
|
The Goal of the Project
|
|
The goal of this
project is to implement an intelligent
software package that handles online disputes
in an automated manner. The following are some
of the recommendations that can be suggested:
-
the framework
should be developed according to current
practice in law in order to avoid further
requests for dispute resolution at higher
level;
-
whenever possible,
automating the existing dispute
resolution;
-
the legal
framework should not only be a mediation
space, but it should also increase the
level of expertise of the mediator;
-
the technology
used must increase the trust in the
resolution process.
|
|
Papers
|
- I. A.
Letia, A. Groza - A Planning-based Approach
for Enacting World Wide Argument Web, in 2nd
International Symposium on Intelligent
Distributed Computing (IDC08),
Catania, Italy, September, Studies
in
Computational Intelligence, pages 137-146, Springer, 2008.
- A. Groza
- Q-learn Argumentation Schemes for Car Sales
Dialogues in the IEEE International
Conference on Intelligent Computer
Communication and Processing (ICCP08),
257-260, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, August,
2008.
- A. Groza
- Designing Electronic Markets for
Defeasible-based Contractual Agents,
European Summer School in Logic,
Language, and Information (ESSLLI),
Hamburg,
Germany, August, 2008.
- I. A.
Letia, A. Groza - Contextual Extension with
Concept Maps in the Argument Interchange
Format Ontology,
Argumentation in Multi-Agent Systems (ArgMAS),
Estoril, Portugal, May, 2008.
- A. Groza
- A Computational Model for World Wide
Argument Web, 13th Estonian Winter School in
Computer Science (EWSCS08),
Palmse, Estonia, 2008.
- I. A.
Letia, A. Groza - Structured Argumentation in
a Mediator for Online Dispute Resolution, In M. Boldoni, T. Son, B.
Riemsdijk, M. Winikoff (eds.) Declarative Agents,
Languages and Technologies V, Selected,
Revised and Invited Papers LNAI 4897, pages
193-200, Springer, 2007.
- A.
Letia, A. Groza - Planning with Argumentation
Shemes in Online Dispute Resolution, 3rd IEEE
International Conference on Intelligent
Computer, Communication and Processing, (ICCP07), Cluj-Napoca, Romania,
September, 2007.
- I. A.
Letia, A. Groza - Exploiting Rough
Argumentation in an Online Dispute Resolution
Mediator, International Conference on Rough
Sets and Emerging Intelligent Systems
Paradigms (RSEISP07), Warsaw, Poland, June, 2007, LNAI 4585,
Springer, 2007, 697-706 (abstract).
- A. Groza
- Towards Mediation with Extended
Temporal Defeasible Logic,
Advanced Course on Artificial Intelligence
Summer School (ACAI 07), Leuven,
Belgium, 2007.
- I. A.
Letia, A. Marginean, A. Groza - Z-Based Agents
for Service Oriented Computing, In: J Huang, R
Kowalczyk, Z Maamar, D Martin, I Mueller, S
Stoutenburg, K Sycara (eds), Service-Oriented
Computing: Agents, Semantics, and Engineering,
LNCS 4504, Springer, 2007, 160-174.
- I. A.
Letia, A. Groza - An argumentative System for
Online Dispute Resolution, CSCS-16, Bucuresti, Romania, May, 2007.
- I. A.
Letia, A. Groza - Structured Argumentation in
a Mediator for Online Dispute Resolution, DALT2007, Honolulu, USA, May, 2007 (pdf).
|
|
Software
|
Temporal Defeasible Logic (TeDeLo)
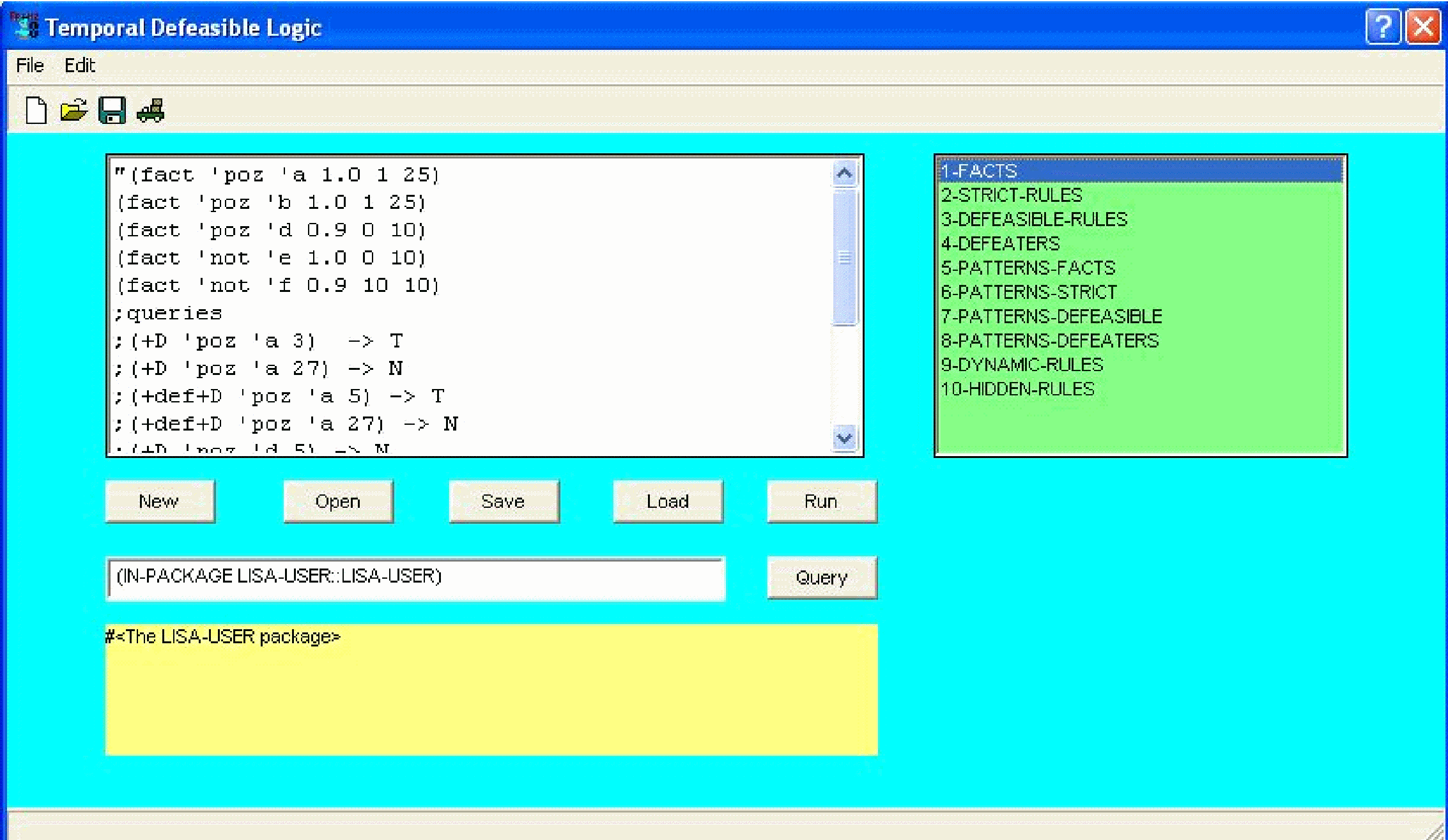
Download: tdl-0.1.2.tar.gz
Requires: LISA, Allegro LISP (for GUI)
Designing Electronic Markets for Contractual
Agents (DEMCA)
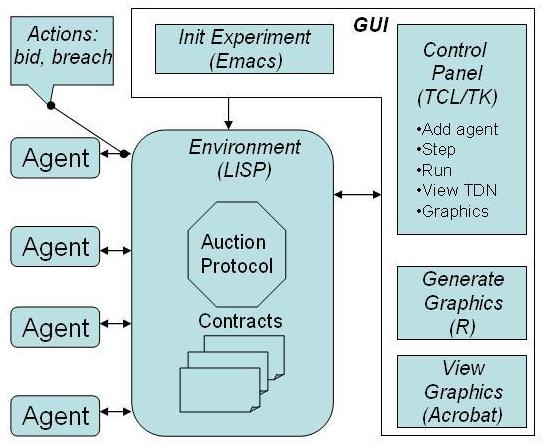
Download:
demca-0.8.tgz
Tested on RedHat 9.0:
Requires:
- gcl
2.6.5
- emacs
21.2.1
- acrobat
reader
- TCL/TK
- R 2.0.0
Arguments in
Fuzzy Description Logic
|
|

adrian.groza@cs.utcluj.ro
|




![]()
